Carcinogenic PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) contaminate the tap water of over 100 million Americans. Also, Europe, Asia and Australia suffer from these hard-to-remove ‘forever chemicals'. New PFAS hot spots are identified daily, exposing nearby populations to serious health risks. Several hundred billion USD are estimated to remove PFAS from our tap water in the US alone. PFAS costs Europe more than €50 billion a year in health problems. Current water treatment solutions are struggling with high operating costs, large volumes of concentrated PFAS waste, and reliability.
CERAFILTEC now proved with its Active Cake Layer Filtration (ACLF) process through various tests over the past 9 months the effective and low-cost removal of different PFAS chemicals including long-chain PFOS, PFOA, PFHxA, and HFPO-DA (GenX). There are also promising results for short-chain PFAS chemicals, e.g. PFBA and PFBS, which will be published after the pilot completion at a customer site.
The ACLF process has been established by CERAFILTEC team members over the last decade for the selective removal of dissolved ions. Large plants with over 400,000 m³/d (~100 MGD) total capacity are operating successfully where the ACLF operation has become the go-to solution due to substantial cost savings. The same process also works for the removal of PFAS molecules as well as Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC), Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC), Trihalomethane (THM), humic acids, pharmaceutical residues, odor, taste, and color. Just the adsorbent changes to Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC).
Activated carbon is already known to be an effective adsorbent for the removal of PFAS chemicals. CERAFILTEC's ACLF process now optimizes how the adsorbent is utilized: Maximizing specific surface areas and shortening adsorption pathways. This is done through covering the ceramic flat sheet membrane with a very thin and loose coating of PAC. All water must pass through this coating. This process is only possible with ceramic flat sheet membranes. It yields highly effective PFAS removal rates and immense cost savings over Granular Activated Carbon (GAC), Ion Exchange (IX), and Reverse Osmosis (RO) processes.
The highly effective and efficient adsorption capabilities are based on two facts:
Both conditions are perfectly combined in CERAFILTEC's ACLF process for the first time.
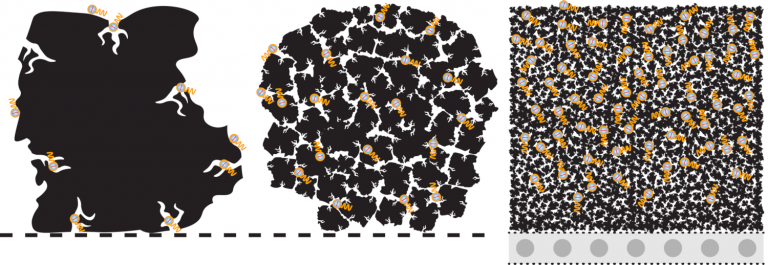
ADSORBED PFAS MOLECULE(S)
GRANULAR ACTIVATED CARBON (GAC) PARTICLE
REAGGLOMERATED GRANULAR ACTIVATED CARBON (R-GAC) PARTICLE
POWDERED ACTIVATED CARBON (PAC) FILTER BED
PORE
COMMON CARRIER LAYER
CERAMIC ULTRAFILTRATION LAYER
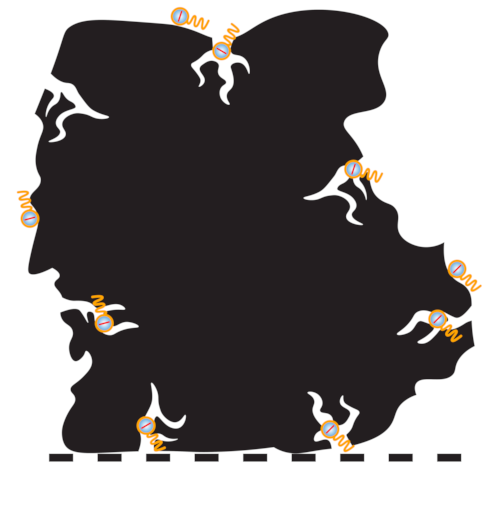

ADSORBED PFAS MOLECULE(S)
GRANULAR ACTIVATED CARBON (GAC) PARTICLE
PORE
COMMON CARRIER LAYER
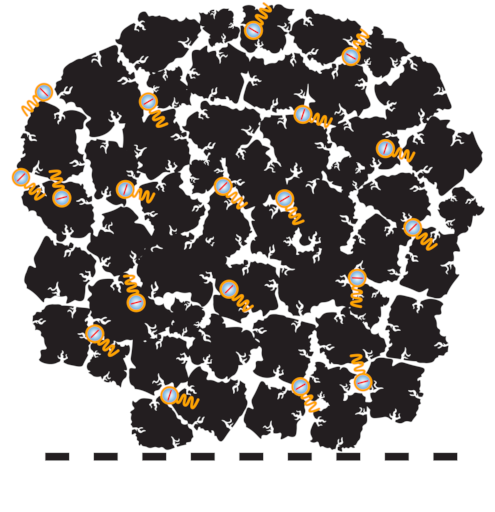
ADSORBED PFAS MOLECULE(S)
REAGGLOMERATED GRANULAR ACTIVATED CARBON (R-GAC) PARTICLE
PORE
COMMON CARRIER LAYER
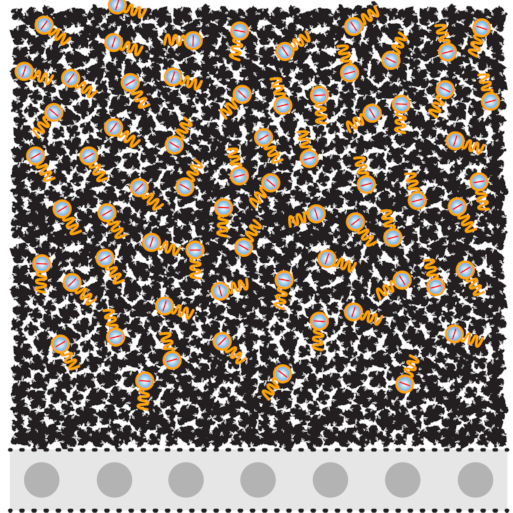
ADSORBED PFAS MOLECULE(S)
POWDERED ACTIVATED CARBON (PAC) FILTER BED
PORE
CERAMIC ULTRAFILTRATION LAYER
The ideal utilization of the activated carbon adsorbent leads to the best total cost of ownership as well as safe and most environmentally-friendly operation.
| Granular Activated Carbon |
Ion Exchange |
Reverse Osmosis |
CERAFILTEC ACLF |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAPEX savings | o | - | - | + |
| OPEX savings | o | - | - | + |
| Removal of long-chain PFAS | + | + | + | + |
| Removal of short-chain PFAS | - | o | + | + |
| Adaptability to PFAS feed fluctuations | - | - | + | + |
| PFAS disposal* | + | - | - | + |
| Granular Activated Carbon | Ion Exchange | Reverse Osmosis | CERAFILTEC ACLF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAPEX savings | o | - | - | + |
| OPEX savings | o | - | - | + |
| Removal of long-chain PFAS | + | + | + | + |
| Removal of short-chain PFAS | - | o | + | + |
| Adaptability to PFAS feed fluctuations | - | - | + | + |
| PFAS disposal* | + | - | - | + |
* Ion Exchange resin must be regenerated with chemicals which produced toxic liquid waste volumes contaminated with PFAS;
Reverse Osmosis produces about 10-15% reject stream, concentrated with PFAS
* Ion Exchange resin must be regenerated with chemicals
which produced toxic liquid waste volumes contaminated with
PFAS; Reverse Osmosis produces about 10-15% reject stream,
concentrated with PFAS
PFAS ‘forever chemicals” are a serious and proliferating drinking water contamination issue of carcinogenic chemicals. These highly toxic substances have been used in hundreds of industrial processes and consumer products for several decades and recently have been linked to cancer, birth defects, ineffectiveness of vaccines, and immune deficiencies. Further, literature suggests PFAS exposure exacerbating the effects of Covid. Today, PFAS has become omnipresent and is found in tap water of over 100 million Americans and in Europe, Asia, and Australia. The American Water Works Association estimates the capital investment to remove PFAS from US drinking water to reach up to $370 billion and annual operating costs to exceed $12 billion per year. CERAFILTEC is confident that this widespread water contamination and health risks can be solved at much lower required investment and much lower operating costs via CERAFILTEC's ACLF process.
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Default. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information